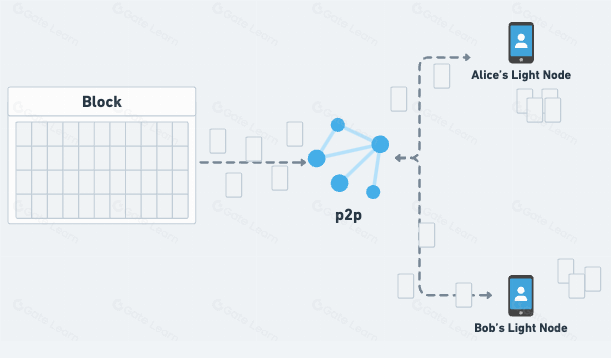
Data Availability Sampling (DAS) is an innovative solution aimed at enhancing the efficiency and security of blockchain networks. While the term might sound complex, breaking it down reveals that DAS addresses a simple question: How can we ensure that all data in a blockchain network is available and accessible without burdening every participant with storing it all?
Let’s explore what DAS is, why it’s important, and how it works in the world of blockchain in a straightforward, non-technical way.
What Is Data Availability Sampling (DAS)?
To understand DAS, think of a public library system. In a library, not every branch needs to hold a copy of every book in the system, but all books should be available somewhere. If one branch doesn’t have a book you want, it can request it from another. Similarly, in a blockchain, not every node (computer on the network) needs to store the entire blockchain’s data as long as the data is available when needed.
Data Availability Sampling (DAS) is a technique that allows nodes in a blockchain network to verify the availability of data without having to store or check the entire data set. Instead, they “sample” small portions of the data to confirm that the entire data block is accessible. This approach helps ensure that a blockchain network can handle large amounts of data efficiently without requiring every node to hold a complete copy of all information.
Purpose of Data Availability Sampling
In traditional blockchains, every node stores the full data of every block in the blockchain. While this helps maintain data integrity, it can also slow down the network and demand large storage requirements, which isn’t feasible as blockchains grow. DAS was designed to solve this problem by allowing nodes to participate in verifying data availability without storing every single piece of data themselves.
The primary goals of DAS are:
- Scalability: As blockchains expand and handle more transactions, the data load on each node increases. DAS reduces the need for nodes to store all data, making it easier to scale blockchain networks without sacrificing speed or security.
- Decentralization: By reducing the storage burden, DAS encourages more users to participate in the network as nodes, leading to a more decentralized system with greater network security.
- Efficiency: DAS allows blockchains to handle data more efficiently. Instead of every node verifying and storing every piece of information, nodes only verify small samples to confirm that the data is available.
In essence, DAS lets a blockchain network grow without overwhelming every participant.
How Does Data Availability Sampling Work?
Using the library analogy, let’s say each branch of a library randomly checks a few books to ensure they are present and available. If a few random samples show that the books are in place, the entire system can assume that all other books are available, even if each branch doesn’t store every book.
In DAS, nodes “sample” parts of a data block instead of storing the entire thing. By randomly checking small parts of a block, a node can statistically verify that the whole block’s data is accessible. If multiple nodes conduct these small checks and find the data is available, it’s highly likely that the complete data is accessible, even if no single node holds it all.
Real-World Examples of Data Availability Sampling
Data Availability Sampling is a relatively new concept and is primarily being explored in experimental and emerging blockchain projects. A few prominent examples include:
- Ethereum’s Data Availability Sampling: Ethereum, one of the most widely used blockchain networks, is investigating DAS to help scale its network. Ethereum developers aim to implement DAS as part of their “sharding” strategy, where the network is divided into smaller parts or “shards” to make data management more efficient. DAS would enable each shard to verify data availability without storing all of it, making the network more scalable.
- Celestia’s Data Availability Sampling: Celestia, a new blockchain project designed for modular blockchains, uses DAS at its core. Rather than building a single, monolithic blockchain, Celestia divides blockchain components, allowing each to perform its task independently. DAS is used to verify data availability across these modular parts, so nodes only need to verify samples of data instead of everything. This setup allows for better scalability and decentralization, making Celestia an ideal project for developers building custom blockchain applications.
- Polygon (Matic Network): Polygon, a blockchain platform focused on scalability, is also exploring the potential of DAS for expanding its data-handling capabilities. As more decentralized applications (DApps) are built on Polygon, DAS could help reduce the load on each node, making it easier to scale the network.
Why Is Data Availability Sampling Important?
Data Availability Sampling is essential for the future of blockchain for several reasons:
- Improved User Experience: With DAS, networks can handle more users and transactions without slowing down. This is crucial as blockchains become more mainstream and support a wide variety of applications, from finance to gaming.
- Lower Storage Requirements: DAS reduces the need for every node to store massive amounts of data. This makes it easier for more users to participate in the network without investing in expensive storage equipment, encouraging greater decentralization.
- Increased Security and Reliability: By ensuring data availability through sampling, DAS maintains the network’s security and reliability. Nodes can confirm that data is available, preventing issues where users might lose access to information or transactions.
- Scalability for Future Growth: As blockchains grow in popularity and applications, they must handle larger volumes of data. DAS enables them to scale effectively without compromising performance or decentralization, making it a cornerstone for future blockchain expansion.
The Future of Data Availability Sampling
Data Availability Sampling holds immense potential for the blockchain industry, especially as networks look to support a broader range of applications and users. By reducing the storage burden on nodes and ensuring data availability through sampling, DAS addresses two critical challenges for blockchain networks: scalability and decentralization.
As more projects like Ethereum, Celestia, and Polygon experiment with DAS, we’re likely to see even more innovative uses of this technology. Over time, DAS could become a standard approach for managing data in blockchain networks, allowing these decentralized systems to grow and serve millions of users without compromising on speed, security, or reliability.
In Summary
Data Availability Sampling (DAS) is a breakthrough technology that allows blockchain nodes to confirm data availability without storing or verifying the entire dataset. This approach is key for the future scalability of blockchain networks, ensuring they can handle more transactions and users while staying secure and decentralized. With projects like Ethereum, Celestia, and Polygon adopting DAS, this technique is set to play a crucial role in making blockchain accessible and efficient for everyone.
A.k.a – alpha girl. Vinita is the founder of Alphachaincrypto. An English Lit Majors, Vinita bumped into Web3 in 2020 only to realise that tech was her calling. Later, Mathreja worked for some notable brands like Near Education, Biconomy, CoinDCX and top of the line crypto start ups.