BRICS Pay is a transformative payment system developed by the BRICS nations—Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa—to streamline cross-border transactions within this bloc. The core goal of BRICS Pay is to enable direct transactions among these economies without relying on traditional, dollar-dominated financial infrastructures, empowering BRICS countries to gain financial independence and reduce exposure to Western-controlled financial systems.
At a broader level, BRICS Pay aims to decrease dependence on existing financial frameworks like SWIFT, which are vulnerable to sanctions and Western influence. With a combined GDP exceeding $26 trillion as of 2024—equivalent to nearly 37% of the global economy—BRICS economies wield considerable power. If BRICS Pay is successfully integrated across these nations, it could redefine global trade by minimizing intermediary currencies and cutting costs associated with currency conversion, particularly with the U.S. dollar.
Political and Economic Foundations of BRICS Pay
The impetus for BRICS Pay lies in both economic aspirations and political strategies, largely as a response to U.S. dollar dominance in global trade and finance.
For decades, the U.S. dollar has been the world’s primary reserve currency, central to international trade and finance. This dominance grants the United States significant control over global financial transactions. While BRICS nations are economically powerful in their own right, the dollar-based financial system limits their financial autonomy. Countries relying on the dollar can face severe economic consequences if sanctions are imposed—such as the ones on Russia, which restricted access to SWIFT and dollar transactions.
BRICS Pay aims to circumvent these limitations by creating a direct payment system that allows transactions in local currencies rather than relying on the U.S. dollar. This system offers BRICS nations a safeguard against potential economic restrictions, allowing them to conduct business on their terms. In essence, BRICS Pay serves as an “economic Plan B,” enabling these countries to build a self-sustaining financial ecosystem.
From a political standpoint, BRICS Pay represents a collective effort to limit dependency on a financial system influenced by U.S. policies. By advancing BRICS Pay, these nations signal their desire for a more balanced, multipolar financial system, advocating for a less U.S.-centric model that provides alternatives for trade and commerce. Ultimately, this move underscores a commitment to economic sovereignty, flexibility, and a reduction in political leverage held by any single nation over others.
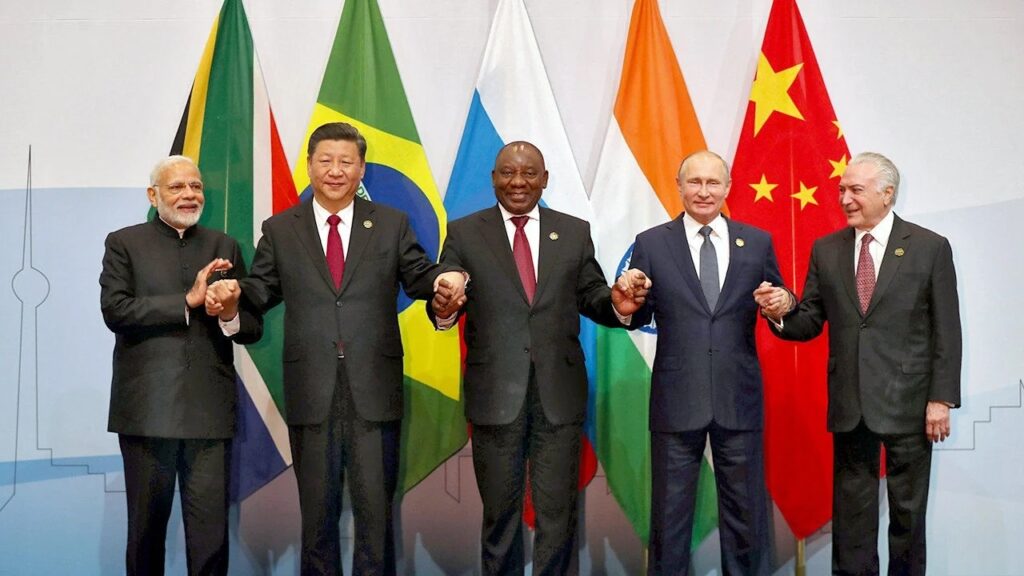

BRICS Summit 2023
Key Features of BRICS Pay
BRICS Pay envisions a cohesive digital payment platform accessible across all BRICS countries, empowering users to conduct transactions directly in their local currencies and eliminating the need for frequent currency conversions.
- Digital Wallet Integration: Users access BRICS Pay through a digital wallet linked to their local bank accounts, allowing seamless fund management and easy payment.
- Multiple Payment Methods: BRICS Pay supports digital payment methods, including QR code-based transactions, enhancing convenience for cross-border payments.
- Local Currency Transactions: By facilitating direct transactions in local currencies, BRICS Pay bypasses the U.S. dollar, reducing foreign exchange risks and supporting currency independence within each nation.
- Economic Strengthening: BRICS Pay promotes the use of domestic currencies, reinforcing the local economies and bolstering national currency value.
- Cost and Efficiency Benefits: The system is designed to streamline currency exchanges within the BRICS economies, potentially reducing transaction fees and improving settlement times compared to conventional banking methods.
This platform utilizes cutting-edge digital wallet technology, QR code-based payments, and frameworks that allow users to connect directly to their banks. While specific technical infrastructure details are still under development, BRICS Pay is expected to employ secure transaction protocols and may incorporate blockchain technology to ensure transparency and reduce transaction costs across borders.
There has been speculation about integrating Ripple’s XRP as a potential blockchain backbone due to its established infrastructure and regulatory compliance. However, adoption will depend on factors like regulatory clarity, security, and technology compatibility across BRICS economies.
Potential Advantages of BRICS Pay
The establishment of BRICS Pay offers multiple strategic benefits, enhancing both the economic independence and financial resilience of member countries.
- Reduced Dependence on Western Financial Systems: By building an independent transaction network, BRICS nations can bypass Western-dominated systems and mitigate the impact of potential economic sanctions.
- Strengthening Local Currencies: BRICS Pay incentivizes the use of domestic currencies, contributing to their stability and gradually reducing reliance on the U.S. dollar in international transactions.
- Enhanced Trade within the Bloc: The platform simplifies payment processing, making cross-border commerce within BRICS more accessible and attractive for businesses.
- Scaling Digital Transactions: In 2023, digital payments across BRICS economies reached $3.25 trillion, demonstrating a 26.1% growth year-on-year. This surge highlights the region’s digital transformation, setting a strong foundation for BRICS Pay to facilitate seamless intra-bloc transactions.
- Future Growth Projections: Digital payment volumes within BRICS economies are projected to grow significantly, potentially reaching $39.3 trillion by 2032. With China anticipated to contribute nearly half of this volume, the rising transaction scale bolsters the potential adoption of BRICS Pay across these economies.
Challenges Facing BRICS Pay Implementation
While BRICS Pay holds promise, several hurdles must be addressed to ensure its successful rollout and long-term viability.
- Diverse Financial Systems: Each BRICS nation has unique financial structures and regulatory standards, which could complicate the harmonization needed for BRICS Pay. However, many BRICS nations have begun experimenting with Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), potentially easing the integration process.
- National Interests and Regional Tensions: Varying priorities and political dynamics could impact cooperation. Although political tensions exist, particularly between India and China, regular dialogues within the BRICS context have fostered progress.
- Currency Volatility: BRICS currencies can be unstable, posing potential risks for cross-border transactions. Without a stabilizing mechanism like the U.S. dollar, currency volatility could challenge the system’s reliability and effectiveness.
- Technical Standardization: Establishing a unified, secure technological infrastructure that meets the needs of all five countries will be crucial. As digital currency and blockchain technologies evolve, BRICS Pay may integrate new innovations to enhance its reach and functionality.
Conclusion
BRICS Pay represents a bold step toward a more balanced, multipolar financial landscape, where BRICS nations can conduct cross-border trade and transactions free from dependency on dollar-centric financial systems. By fostering economic resilience and enhancing digital payment infrastructure, BRICS Pay has the potential to reshape global commerce, creating a robust intra-bloc trade network that stands independently of Western influence.
As BRICS nations continue to develop this payment system, BRICS Pay could pave the way for other countries to explore similar alternatives, advancing a more diverse, multipolar world economy.
A.k.a – alpha girl. Vinita is the founder of Alphachaincrypto. An English Lit Majors, Vinita bumped into Web3 in 2020 only to realise that tech was her calling. Later, Mathreja worked for some notable brands like Near Education, Biconomy, CoinDCX and top of the line crypto start ups.





